Recommendation Info About Do AC Circuits Have Polarity

Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding the Basics of AC and DC
Okay, let's dive right into it. The question of whether AC (Alternating Current) circuits have polarity is a common one, especially for those just starting out in the world of electronics. To really grasp this, we need to quickly touch on what AC and DC (Direct Current) are all about. Think of it like this: DC is like a one-way street for electrons, flowing steadily in a single direction. A battery is a classic example of DC, with a positive (+) and a negative (-) terminal always maintaining their roles.
Now, AC is the rebellious cousin of DC. Instead of a steady flow, the electrons in AC are constantly changing direction, oscillating back and forth. This change happens at a specific frequency, typically 50 or 60 times per second (Hertz) depending on where you are in the world. The power that comes out of your wall socket? Yep, that's AC. It's the reason your lights flicker (though hopefully imperceptibly!) and why you can power all sorts of devices.
So, what does all this have to do with polarity? Well, it all boils down to that changing direction. With electrons constantly switching their flow, the traditional idea of a fixed positive and negative doesn't quite hold water. Its more dynamic, morefluid, if you will. Think of it like a seesaw, constantly going up and down. There isn't a permanently 'up' or 'down' side, just phases of movement.
Therefore, we can say that in the strictest sense, AC circuits don't have a fixed polarity like DC circuits do. This doesn't mean polarity is irrelevant, though! It just manifests in a different way, as we'll explore further.

The Dynamic Nature of AC "Polarity"
2. Phases and Reference Points
So, weve established that AC doesn't have a fixed positive and negative. But that doesn't mean we can just throw caution to the wind and connect things willy-nilly! There's a concept called "phase" that comes into play. Imagine multiple AC signals flowing through a circuit at the same time. These signals can be "in phase" (moving together) or "out of phase" (offset from each other). This phase relationship becomes really important when dealing with things like three-phase power systems (used in industrial settings) or audio signals.
Think of it like a synchronized swimming routine. The swimmers are all performing similar movements, but some might be slightly ahead or behind others. That relative positioning is crucial for the overall effect! Similarly, the phase relationship between AC signals is essential for the circuit to function correctly.
Another important aspect is the idea of a "reference point." In many AC circuits, particularly those connected to the mains supply, one wire is designated as "neutral," which is generally kept near ground potential. The other wire is the "live" or "hot" wire, which carries the alternating voltage. While the voltage on the live wire is constantly changing between positive and negative relative to neutral, it's still important to connect appliances correctly. Incorrect wiring can lead to shocks or damage to equipment.
You might hear the term "polarity" used loosely in some AC contexts. For example, connecting a polarized capacitor backwards in an AC circuit is a recipe for disaster. Even though the voltage is alternating, the capacitor is designed to handle voltage primarily in one direction. So, while AC itself lacks fixed polarity, components within an AC circuit may be sensitive to the direction of the applied voltage, thus requiring correct orientation.

Why Proper Wiring Matters (Even Without Fixed Polarity)
3. Safety First!
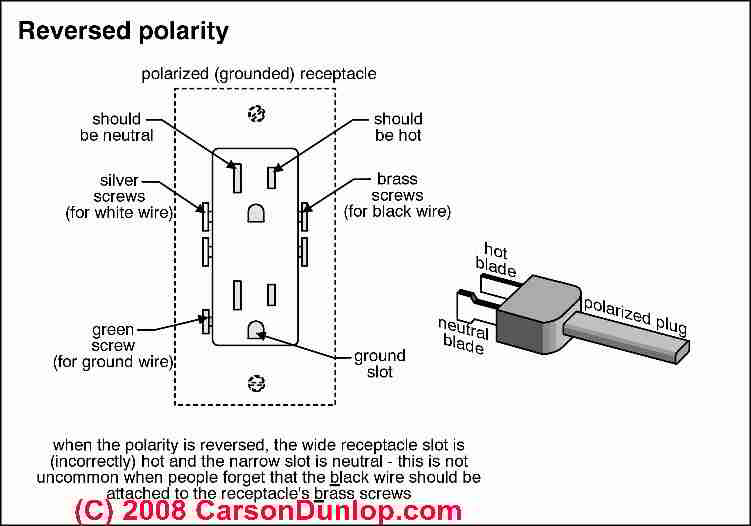
Even though AC circuits don't have a fixed polarity in the DC sense, proper wiring is absolutely crucial for safety and functionality. Lets consider a standard household outlet. One slot is slightly wider than the other. This is intentional! The wider slot is the neutral wire, which is connected to ground at the service panel. The narrower slot is the hot wire, which carries the alternating voltage. The third, round hole is the ground connection, providing a safety path for current in case of a fault.
When you plug in an appliance, the hot wire provides the power to operate it, while the neutral wire provides the return path for the current. The ground wire provides an extra layer of protection. If, for example, a wire inside the appliance comes loose and touches the metal casing, the ground wire will provide a low-resistance path for the current to flow back to the service panel, tripping the circuit breaker and preventing a potentially dangerous shock.
Incorrect wiring can have serious consequences. If the hot and neutral wires are reversed, the appliance may still operate, but the metal casing could become energized, posing a shock hazard. Similarly, if the ground wire is disconnected or improperly connected, the safety protection is lost. Thats why electrical work should always be performed by a qualified electrician who understands and follows proper wiring practices.
Think of it like driving a car. Even though you don't have a fixed 'positive' or 'negative' steering direction, you still need to steer correctly to avoid crashing! Likewise, in AC circuits, understanding the roles of the hot, neutral, and ground wires is essential for safe and reliable operation.
Common Misconceptions About AC and Polarity
4. Clearing Up the Confusion
One of the most common misconceptions is that since AC doesn't have a fixed polarity, you can connect anything any which way. As we've discussed, this is definitely not the case! While the alternating nature of the current does mean there's no constant positive or negative terminal like in a DC battery, the phase relationships, reference points (like neutral and ground), and component sensitivities all necessitate proper wiring and connection practices.
Another misunderstanding is that "polarity" in AC is completely meaningless. While the term might not be strictly accurate in the DC sense, it's often used to describe the relative phase or voltage between different points in a circuit. Thinking of it more broadly as a relationship rather than a fixed characteristic can help clarify things.
Some people also believe that AC is inherently more dangerous than DC because of its higher voltage. While it's true that AC can be lethal, the danger is more about the amount of current flowing through the body, not necessarily whether it's AC or DC. High-voltage DC can be just as dangerous, if not more so, than high-voltage AC.
Finally, theres a misconception that all AC components are polarity-insensitive. This simply isn't true. As mentioned earlier, polarized capacitors are a prime example of components that require correct orientation, even in AC circuits. Other components, like diodes and some types of transistors, also have polarity requirements that must be observed.
![[Grade 12 Physics Electric Circuits] How Exactly Do I Determine The [Grade 12 Physics Electric Circuits] How Exactly Do I Determine The](https://preview.redd.it/grade-12-physics-electric-circuits-how-exactly-do-i-v0-a2ul18l39tu91.jpg?auto=webp&s=16bdc437b4c36843d38028b48398dbecbcae802e)
Practical Implications and Everyday Examples
5. AC in the Real World
So, how does all this AC "polarity" (or lack thereof) stuff manifest in our everyday lives? Well, consider the simple act of plugging in your phone charger. The charger itself converts AC voltage from the wall outlet into DC voltage to charge your phone's battery. The internal circuitry of the charger is carefully designed to handle the AC input and ensure that the DC output is properly regulated.
Think about audio equipment. Speakers typically have two terminals, often marked with "+" and "-". While the signal feeding the speaker is AC, connecting the wires incorrectly (reversing the "polarity") can cause the speakers to be "out of phase," resulting in a loss of bass response and a muddy sound. This isn't a matter of damaging the speaker, but rather one of optimizing the audio quality.
Solar panels are another fascinating example. Solar panels generate DC electricity when exposed to sunlight. This DC electricity is then typically converted to AC using an inverter so that it can be fed into the grid or used to power AC appliances. The inverter needs to carefully synchronize the phase of the AC output with the grid to ensure a smooth and efficient flow of power.
Even something as seemingly simple as a light bulb involves AC. Incandescent bulbs dont care about polarity (hence why you can screw them in either way). But newer LED bulbs often have more complex circuitry inside, including rectifiers and drivers that convert the AC input into a stable DC voltage to power the LEDs. These circuits are designed with specific "polarity" considerations in mind, even though the wall socket provides AC.

Does A Capacitor Have Polarity? ElectronicsHacks
FAQ
6. Q
A: While your device might still work, reversing the hot and neutral wires in a standard wall outlet is extremely dangerous. It can energize the metal casing of appliances, creating a shock hazard. Always ensure proper wiring or consult a qualified electrician.
7. Q
A: Connecting a polarized capacitor backwards in any circuit, AC or DC, is a bad idea. The capacitor is designed to withstand voltage in only one direction. Reversing the polarity can cause the capacitor to overheat, leak, and potentially explode. It's not a pretty sight (or sound!).
8. Q
A: Yes! While AC itself doesn't have fixed polarity, many components within AC circuits are polarity-sensitive. Polarized capacitors are the most common example, but other components like diodes and some transistors also require correct orientation. Additionally, devices with complex internal electronics, like audio amplifiers or power supplies, can be sensitive to the phase relationship of the AC input.